The nutraceutical industry, encompassing dietary supplements, functional foods, and beverages, is experiencing exponential growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health and wellness. However, behind the glossy packaging and health claims lies a complex global supply chain fraught with unique risks. Unlike pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals often navigate a less stringent regulatory landscape, which can amplify vulnerabilities related to raw material sourcing, manufacturing, and distribution. Managing these nutraceutical supply chain risks is paramount for ensuring product quality, consumer safety, and brand reputation.
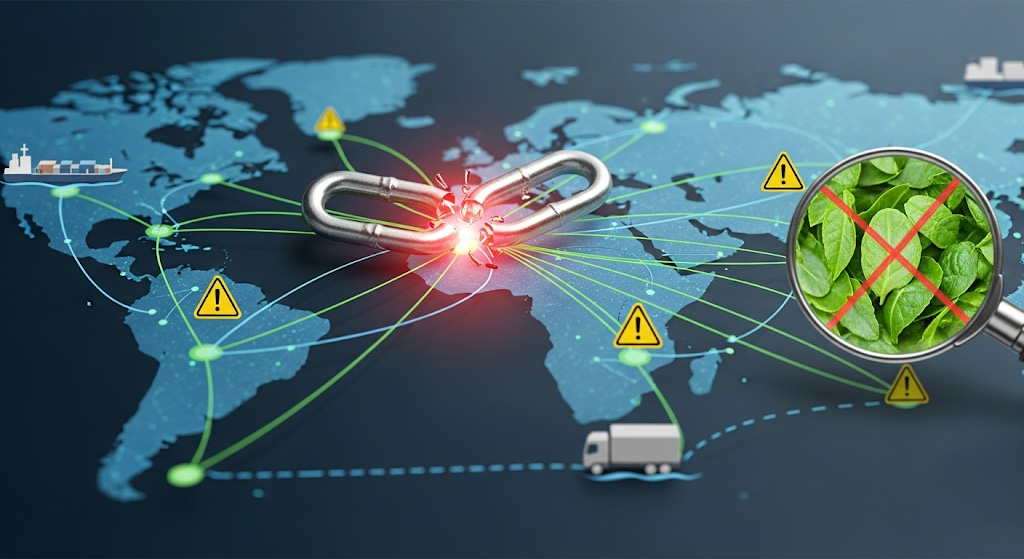
Uderstanding the Nutraceutical Supply Chain: A Landscape of Interconnected Risks
The nutraceutical supply chain is an intricate web of interconnected stages, each presenting its own set of potential pitfalls. From farm to consumer, a disruption at any point can cascade, leading to significant financial losses, regulatory non-compliance, and damage to brand trust.
1. Raw Material Sourcing Risks
The journey of a nutraceutical product begins with its raw materials, and this initial stage is often the most susceptible to a variety of risks. The global nature of sourcing, combined with the often-natural origins of ingredients, introduces unique challenges.
-
Adulteration and Fraud: This is perhaps the most significant risk. Raw materials, especially high-value botanical extracts or rare ingredients, are susceptible to economically motivated adulteration (EMA). This can involve diluting expensive ingredients with cheaper substitutes, adding synthetic compounds, or mislabeling species. For example, turmeric extract might be spiked with synthetic curcumin, or a rare herb might be substituted with a common, ineffective plant. This not only compromises product efficacy but can also pose severe health risks if harmful or undeclared substances are introduced.
-
Contamination: Raw materials, particularly botanicals or minerals, can be contaminated with heavy metals (e.g., lead, arsenic, cadmium, mercury), pesticides, microbial pathogens (e.g., E. coli, Salmonella), or mycotoxins (e.g., aflatoxins). These contaminants can originate from soil, water, harvesting practices, or improper storage. Ensuring the purity of raw materials requires rigorous testing at the point of origin and upon arrival at the manufacturing facility.
-
Supplier Reliability and Transparency: Relying on a limited number of suppliers, or suppliers with opaque practices, increases risk. Issues like sudden price increases, quality inconsistencies, delayed shipments, or even supplier bankruptcy can disrupt production. Lack of traceability through the entire raw material journey, from farm to processor, makes it difficult to pinpoint the source of problems.
-
Geopolitical and Environmental Factors: Raw material availability can be heavily influenced by events in sourcing regions. Natural disasters (floods, droughts), political instability, trade wars, or pandemics can disrupt cultivation, harvesting, and transportation, leading to supply shortages and price volatility. For instance, specific botanical ingredients might only grow in certain climates, making their supply vulnerable to regional crises.
-
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing: Growing consumer demand for ethically and sustainably sourced products introduces risks related to deforestation, overharvesting of endangered species, poor labor practices, or lack of fair trade. Brands face reputational damage if their supply chain is found to be linked to unethical practices.
2. Manufacturing and Production Risks
Once raw materials arrive, the manufacturing process itself presents several layers of risk that can compromise product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance.
-
Cross-Contamination: In facilities producing multiple products, inadequate cleaning protocols or poor material handling can lead to cross-contamination between different batches or products. This is particularly critical for allergen management, where trace amounts of an undeclared allergen can trigger severe consumer reactions.
-
Dosage Inconsistency and Potency Variation: Inaccurate weighing, blending, or encapsulation processes can result in inconsistent dosage of active ingredients. This means some finished products might contain too little of the active ingredient (reducing efficacy) or too much (potentially causing adverse effects). Variations in raw material potency also need to be accounted for during formulation.
-
Microbiological Growth: Nutraceuticals, especially those containing natural extracts or probiotics, are susceptible to microbial growth if environmental controls (temperature, humidity) are not properly managed during manufacturing, packaging, or storage. This can lead to product spoilage and consumer health risks.
-
Equipment Malfunction and Process Failures: Breakdowns in manufacturing equipment, errors in process parameters (e.g., incorrect temperature during drying, improper mixing times), or human error can lead to entire batches being compromised.
-
Lack of cGMP Adherence: Failure to strictly follow Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs) is a major risk. cGMPs cover everything from facility design and maintenance to personnel training, quality control testing, and record-keeping. Non-compliance can result in warning letters, product seizures, and mandatory recalls.
-
Stability and Shelf Life Issues: Inadequate understanding or testing of product stability can lead to active ingredients degrading over time, rendering the product ineffective before its stated expiry date. Factors like heat, light, and moisture can significantly impact stability.
3. Regulatory and Compliance Risks
The regulatory landscape for nutraceuticals is complex and constantly evolving, varying significantly by country and region. Non-compliance is a major risk, leading to legal action, market withdrawal, and significant financial penalties.
-
Labeling and Claims Misrepresentation: Making unsubstantiated health claims, failing to list all ingredients accurately, or misrepresenting the product's dosage on the label are serious violations. Unlike pharmaceutical drugs, nutraceuticals cannot claim to "cure," "treat," or "prevent" diseases, and missteps here are common.
-
Ingredient Approval and Restrictions: Certain ingredients may be permitted in one country but restricted or banned in another. Brands operating globally must navigate these complex differences. New ingredient approvals also vary by region.
-
Documentation and Record-Keeping: Failure to maintain meticulous records of raw material sourcing, manufacturing batch records, quality control tests, and adverse event reports can lead to significant issues during audits and inspections.
-
Adverse Event Reporting (AER) Failures: Brands are often required to report serious adverse events linked to their products to regulatory bodies. Failure to do so promptly and accurately carries legal consequences.
-
Import/Export Compliance: Navigating customs, tariffs, and specific import/export regulations for nutraceuticals can be complex, leading to shipment delays, confiscation, or penalties if not handled correctly.
-
High-Risk Product Category: From a financial perspective, the nutraceutical industry is often categorized as "high-risk" by payment processors and banks due to potential regulatory scrutiny, higher chargeback ratios (e.g., due to customer dissatisfaction with perceived efficacy or automatic renewals), and legal uncertainties around product claims.
4. Distribution and Logistics Risks
Even after a product is manufactured and packaged, the journey to the consumer's hands carries its own set of risks.
-
Temperature and Humidity Excursions: Many nutraceuticals (especially probiotics, enzymes, or certain delicate botanicals) are sensitive to temperature and humidity fluctuations. Improper storage or transportation conditions can lead to product degradation, reduced potency, or spoilage before it reaches the consumer. The "cold chain" for sensitive ingredients is critical.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: Beyond raw materials, disruptions can occur at any point in the logistics chain. This includes port closures, shipping delays, customs issues, transport strikes, fuel price volatility, or even cyberattacks on logistics providers. These can lead to stockouts, lost sales, and increased costs.
-
Inventory Management: Inefficient inventory practices can lead to either stockouts (missed sales opportunities and frustrated customers) or overstocking (leading to product expiry, waste, and increased storage costs). Balancing demand forecasting with production and delivery lead times is crucial.
-
Product Diversion and Counterfeiting: The popularity and value of nutraceuticals make them targets for diversion (selling through unauthorized channels) and counterfeiting. Counterfeit products pose severe health risks, erode consumer trust, and damage brand reputation.
-
Damage and Loss: Products can be damaged during transit due to improper handling, packaging, or accidents. Loss due to theft or misplacement also presents a financial risk.
Mitigating Risks and Building Supply Chain Resilience
Effectively managing these risks requires a proactive, multi-faceted approach focused on transparency, robust quality systems, and strategic partnerships.
1. Robust Supplier Qualification and Management
-
Due Diligence: Implement a comprehensive supplier qualification program. This includes auditing supplier facilities, requesting third-party certifications (e.g., ISO, HACCP, organic), and reviewing their quality control documentation and test results (CoAs).
-
Diversification: Avoid single-source reliance for critical raw materials. Diversify your supplier base to mitigate risks from regional disruptions or supplier issues.
-
Long-Term Partnerships: Foster strong, transparent relationships with key suppliers. This can lead to better communication, preferential treatment during shortages, and greater willingness to share information and invest in quality improvements.
-
Traceability: Demand full traceability of raw materials from farm to finished product. Implementing blockchain technology or advanced tracking systems can enhance transparency.
2. Strict Quality Control and cGMP Adherence
-
In-House Testing and Third-Party Verification: Implement rigorous in-house testing for incoming raw materials and finished products for identity, purity, potency, and contaminants. Additionally, partner with reputable third-party laboratories for independent verification, adding an extra layer of assurance for both compliance and consumer trust.
-
Automated Systems: Utilize automation and advanced manufacturing technologies to minimize human error, improve consistency, and enhance production efficiency.
-
Continuous Monitoring: Implement real-time monitoring of critical process parameters (temperature, humidity, pressure) throughout manufacturing and storage.
-
Employee Training: Invest in ongoing training for all personnel on cGMPs, quality control procedures, and proper handling of ingredients and finished products.
-
Robust Documentation: Maintain meticulous, easily retrievable records for every stage of the supply chain, from raw material receipt to final product shipment.
3. Proactive Regulatory Compliance Strategy
-
Dedicated Regulatory Affairs: Employ or consult with regulatory affairs specialists who can stay abreast of evolving global regulations for nutraceuticals.
-
Labeling Review: Conduct thorough, independent reviews of all product labels and marketing claims to ensure full compliance with target market regulations.
-
Legal Counsel: Engage legal counsel experienced in dietary supplement law to review advertising, website content, and any potentially ambiguous claims.
-
Pre-Market Assessments: For new or complex ingredients, conduct diligent pre-market assessments to ensure regulatory compliance before launching.
4. Supply Chain Resilience and Agility
-
Risk Assessment and Mapping: Conduct regular, comprehensive risk assessments across your entire supply chain to identify potential vulnerabilities (e.g., single points of failure, geopolitical hotspots, climate risks). Map your supply chain to gain full visibility.
-
Contingency Planning: Develop detailed contingency plans for various disruption scenarios (e.g., natural disasters, supplier bankruptcy, transport delays). This includes identifying alternative suppliers, logistics routes, and backup production facilities.
-
Inventory Optimization: Implement smart inventory management strategies, balancing just-in-time principles with adequate safety stock for critical components, especially those with long lead times or high volatility.
-
Technology Adoption: Leverage technology such as supply chain management (SCM) software, predictive analytics, and IoT sensors to gain real-time visibility into inventory levels, shipments, and environmental conditions.
-
Collaboration and Communication: Foster strong communication channels and collaboration with all supply chain partners – from raw material suppliers to distributors and retailers. Transparent information sharing enables quicker responses to disruptions.
5. Ethical Sourcing and Sustainability Initiatives
-
Supplier Codes of Conduct: Establish clear codes of conduct for suppliers covering environmental protection, fair labor practices, and ethical sourcing.
-
Audits and Certifications: Conduct regular ethical and environmental audits of suppliers and prioritize those with reputable sustainability certifications (e.g., Rainforest Alliance, Fair Trade).
-
Transparency Reporting: Consider transparent reporting on your sourcing practices and sustainability efforts to build consumer trust and meet growing demands for corporate social responsibility.
The nutraceutical supply chain, while offering immense opportunities for health and wellness brands, is inherently exposed to a multitude of complex risks. From the authenticity of raw materials and the precision of manufacturing to ever-changing regulations and logistical challenges, each stage demands vigilant oversight. By prioritizing robust risk assessment, implementing stringent quality controls, fostering strong supplier relationships, and building resilient, transparent supply chains, nutraceutical companies can effectively mitigate these challenges. This proactive approach not only safeguards product integrity and ensures consumer safety but also fortifies brand reputation and paves the way for sustainable growth in a competitive global market.
Sure, here's the marketing content about Zhongci Health to add to the end of the article:
Partnering for Success: Your Nutraceutical Supply Chain Solution with Zhongci Health
Navigating the complexities and inherent risks of the nutraceutical supply chain can be a daunting task for any brand. From securing authentic raw materials and ensuring cGMP-compliant manufacturing to managing intricate logistics and staying ahead of evolving regulations, the challenges are continuous. This is where a truly reliable and experienced partner becomes invaluable.
Zhongci Health stands as a leading, vertically integrated nutraceutical manufacturer, providing comprehensive solutions designed to mitigate these risks and streamline your journey from concept to consumer. We are not just a manufacturer; we are a strategic partner committed to safeguarding your brand's integrity and ensuring product excellence at every stage.
Here's how Zhongci Health helps you overcome supply chain challenges:
-
Rigorous Raw Material Vetting: We prioritize source verification and conduct multi-level testing for identity, purity, and contaminants (including heavy metals, pesticides, and microbes) on all incoming raw materials. Our global network of trusted suppliers is continuously audited to ensure ethical sourcing and consistent quality, reducing your exposure to adulteration and supply disruptions.
-
State-of-the-Art cGMP Manufacturing: Our facilities strictly adhere to Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs), ensuring precise formulation, consistent potency, and robust quality control throughout the entire production process. We utilize advanced technology to minimize human error and ensure product stability and safety.
-
Comprehensive Quality Assurance: Beyond cGMPs, our in-house laboratories perform extensive third-party verified testing on finished products for potency, purity, and shelf-life stability. We maintain meticulous documentation for full traceability, providing you with complete confidence in every batch.
-
Regulatory Expertise: Our dedicated regulatory affairs team stays abreast of global compliance requirements. We assist you in navigating complex labeling regulations and ensuring all product claims are substantiated and compliant with target market laws, safeguarding your brand from legal pitfalls.
-
Resilient Logistics Support: We understand the critical importance of a smooth distribution chain. Zhongci Health provides expert guidance on packaging for stability, offers robust inventory management solutions, and helps optimize logistics to protect product integrity during transit, minimizing risks like temperature excursions and shipping delays.
-
Flexible Partnership Models: Whether you require white label solutions for rapid market entry, custom formulations tailored to niche demands, or comprehensive private label services from product development to packaging design, Zhongci Health adapts to your specific needs. Our expertise in creating popular formats like multivitamin gummies, alongside a wide array of other supplement types, positions us as your ideal partner for growth.
By partnering with Zhongci Health, you leverage decades of manufacturing expertise, robust quality systems, and a proactive approach to risk management. This allows you to focus on what you do best – building your brand and connecting with your customers – with the peace of mind that your nutraceutical supply chain is secure, compliant, and optimized for success.