Creatine is one of the most widely researched and effective dietary supplements in the sports and fitness world, recognized for its profound impact on athletic performance and muscle growth. Beyond the gym, ongoing research also reveals its potential benefits for general health and cognitive function. But what exactly is this powerful compound, how is it made, and what does it do inside your body? This article provides a comprehensive look at creatine, demystifying its science, explaining its benefits, outlining its proper usage, and clarifying its mechanism of action.
What Is Creatine
Creatine is a naturally occurring organic acid that plays a crucial role in the body's energy production. It's not a steroid, but rather a compound derived from three amino acids: arginine, glycine, and methionine. Approximately 95% of the body's creatine is stored in skeletal muscle, with smaller amounts found in the brain and testes.

Our bodies produce creatine, and we also obtain it through diet, primarily from animal products like red meat and fish. However, the amounts obtained from diet alone are typically insufficient to maximize the body's creatine stores, which is why supplementation has become popular.
How Creatine Is Made (Synthesis and Production)
Creatine is synthesized naturally within the human body, primarily in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. This internal production process involves a series of enzymatic reactions that combine the three precursor amino acids.
For dietary supplements, creatine is synthetically produced on a large scale. The most common form used in supplements is creatine monohydrate, which is known for its purity, stability, and effectiveness. The industrial production typically involves chemical reactions between sarcosine (a derivative of glycine) and cyanamide. This process yields creatine, which is then purified and micronized (ground into a very fine powder) to improve solubility and absorption. Strict quality control measures are in place during manufacturing to ensure the purity and safety of the final product.
How Creatine Works Its Mechanism of Action
Creatine's primary function in the body revolves around energy production, particularly during short bursts of high-intensity activity. Here’s a breakdown of its key mechanisms:
-
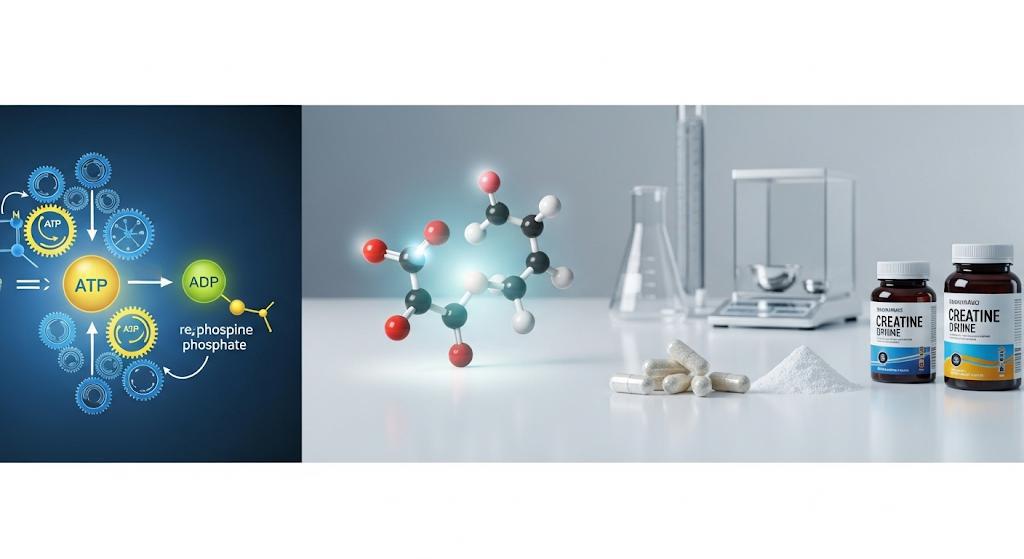
ATP Regeneration (The Energy Currency): Our cells use a molecule called Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) as their immediate energy source. When ATP is used for energy (e.g., during a muscle contraction), it loses a phosphate group and becomes Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP). Our body's stores of ATP are very limited, lasting only a few seconds during intense effort.
-
Creatine Phosphate System: This is where creatine comes in. Inside muscle cells, creatine is converted into creatine phosphate (PCr), a high-energy compound. When ATP levels drop, PCr rapidly donates its phosphate group back to ADP, quickly regenerating ATP.
-
Increased Energy Availability: By enhancing the body's ability to rapidly regenerate ATP, creatine allows muscles to perform at peak intensity for longer durations during activities like weightlifting, sprinting, or jumping. This means you can squeeze out more reps, lift slightly heavier weights, or sustain power output for a few more seconds.
-
Cell Volumization (Hydration): Creatine draws water into muscle cells, leading to an increase in cell volume. This "volumization" is thought to act as an anabolic signal, potentially stimulating protein synthesis and reducing protein breakdown, contributing to muscle growth.
-
Other Potential Mechanisms: Research suggests creatine may also reduce muscle damage and inflammation after exercise, increase levels of anabolic hormones, and improve satellite cell activity (cells involved in muscle repair and growth).
Key Benefits of Creatine
The well-documented benefits of creatine primarily revolve around exercise performance, but extend to other areas of health.
-
Enhanced Strength and Power Output: This is creatine's most recognized benefit. By increasing ATP regeneration, it allows for greater strength gains and explosive power during short, intense bouts of activity.
-
Increased Muscle Mass: Over time, the ability to perform more reps or lift heavier weights translates into greater muscle growth (hypertrophy). The cell volumization effect also contributes to this.
-
Improved Exercise Performance: Beneficial for activities requiring repeated bursts of high intensity, such as weightlifting, sprinting, high-intensity interval training (HIIT), and various team sports.
-
Faster Muscle Recovery: Some studies suggest creatine can help reduce muscle cell damage and inflammation post-exercise, leading to quicker recovery.
-
Brain Health and Cognitive Function: Creatine is stored in the brain and plays a role in brain energy metabolism. Research, though still emerging, indicates potential benefits for memory, intelligence, and reducing fatigue in certain populations (e.g., vegetarians who have lower dietary creatine intake, or those under sleep deprivation). It's also being studied for neuroprotective effects in various neurological conditions.
-
Bone Health: Some evidence suggests creatine supplementation, especially when combined with resistance training, may have positive effects on bone mineral density.
-
Glycogen Resynthesis: Creatine may help increase the rate at which muscles replenish glycogen stores after intense exercise, which is crucial for endurance and recovery.
Usage Guidelines and Recommendations
Creatine is one of the most studied supplements, with clear guidelines for effective and safe use.
-
Form of Creatine:
-
Creatine Monohydrate: This is the most studied and highly recommended form. It's proven effective, safe, and generally the most cost-effective. Other forms (e.g., creatine ethyl ester, creatine HCL) have not consistently shown superior benefits over monohydrate.
-
-
Dosage:
-
Loading Phase (Optional but Recommended): To rapidly saturate muscle creatine stores, take 20 grams per day (divided into 4 doses of 5 grams) for 5-7 days.
-
Maintenance Phase: After the loading phase, or if you skip loading, take 3-5 grams per day consistently. Higher doses (up to 10g/day) may be beneficial for individuals with high muscle mass or very high training volumes, but generally 3-5g is sufficient for most.
-
-
Timing:
-
The timing of creatine intake is less critical than consistent daily use. However, some research suggests taking it around your workout (either pre- or post-exercise) might slightly enhance absorption or effectiveness due to increased blood flow or insulin sensitivity.
-
You can mix creatine powder with water, juice, or your post-workout shake. Taking it with carbohydrates can enhance absorption by stimulating insulin.
-
-
Hydration:
-
Because creatine draws water into muscle cells, it's crucial to drink plenty of water throughout the day when supplementing. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses (2-3 liters) daily.
-
-
Consistency:
-
Creatine works by saturating your muscle stores over time, so consistent daily intake is far more important than precise timing. Skipping days will slow down the saturation process.
-
Safety Side Effects and Who Should Use It
Creatine is generally considered safe and well-tolerated for healthy individuals when taken at recommended dosages. It's one of the most rigorously tested supplements.
-
Common Myths vs. Facts:
-
Kidney Damage: Extensive research consistently shows that creatine does not cause kidney damage in healthy individuals. However, those with pre-existing kidney conditions should consult their doctor before use.
-
Hair Loss: There is no strong scientific evidence to suggest creatine directly causes hair loss or baldness. One study showed an increase in DHT (a hormone linked to hair loss) in rugby players, but more research is needed to confirm this link and its clinical significance in a broader population.
-
Dehydration/Cramps: If adequate water intake is maintained, creatine does not typically cause dehydration or muscle cramps. In fact, by increasing cellular hydration, it might even reduce the risk of cramps.
-
-
Potential Mild Side Effects:
-
Water Retention: Initial weight gain of 1-3 kg (2-6 lbs) is common during the loading phase due to increased water retention in muscles. This is not fat gain.
-
Digestive Issues: Rarely, some individuals may experience mild stomach upset, nausea, or diarrhea, especially with very high single doses. Dividing doses or taking it with food can help.
-
-
Who Should Use Creatine:
-
Athletes & Bodybuilders: Individuals engaging in strength training, power sports, sprinting, or high-intensity interval training.
-
Vegetarians/Vegans: As creatine is found primarily in animal products, vegetarians and vegans often have lower baseline creatine levels and may experience more pronounced benefits from supplementation.
-
Older Adults: Combined with resistance training, it may help preserve muscle mass and strength.
-
Individuals Seeking Cognitive Support: For potential brain health benefits, especially if dietary intake is low.
-
-
Who Should Exercise Caution:
-
Individuals with Kidney Disease: Consult a doctor.
-
Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women: Insufficient research, best to avoid.
-
Children and Adolescents: Generally not recommended unless specifically supervised by a medical professional for therapeutic reasons.
-
Always choose creatine from reputable brands that provide third-party testing for purity and potency.
Conclusion
Creatine stands as a testament to the power of targeted supplementation for enhancing physical performance and potentially broader health. From its natural synthesis in the body and its efficient industrial production as creatine monohydrate, to its pivotal role in rapidly regenerating ATP for explosive energy, its benefits for strength, muscle growth, and recovery are well-established. When used correctly and consistently, creatine is a safe and highly effective supplement that can significantly support your fitness goals and overall well-being. Understanding its mechanisms and adhering to proper usage guidelines will allow you to unlock its full potential.
Authoritative Information Sources:
-
NIH Office of Dietary Supplements (ODS): For general information on creatine.
-
International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN): Publishes extensive position stands on creatine safety and efficacy.
-
Link: https://www.sportsnutritionsociety.org/ (Look for their position stand on creatine)
-
-
National Institutes of Health (NIH) - PubMed: For scientific studies and meta-analyses on creatine.